Semaglutid: Diabetes Treatment and Weight Management
Semaglutid is a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA), a synthetic analog of the naturally occurring hormone GLP-1, which plays a critical role in regulating blood glucose levels. In people with diabetes, GLP-1 secretion or activity may be insufficient, leading to impaired blood glucose control. Semaglutid binds to GLP-1 receptors, mimicking the hormone’s physiological effects, thereby supporting the management of diabetes and aiding in weight control.
Reproductive Health and Hormonal Regulation
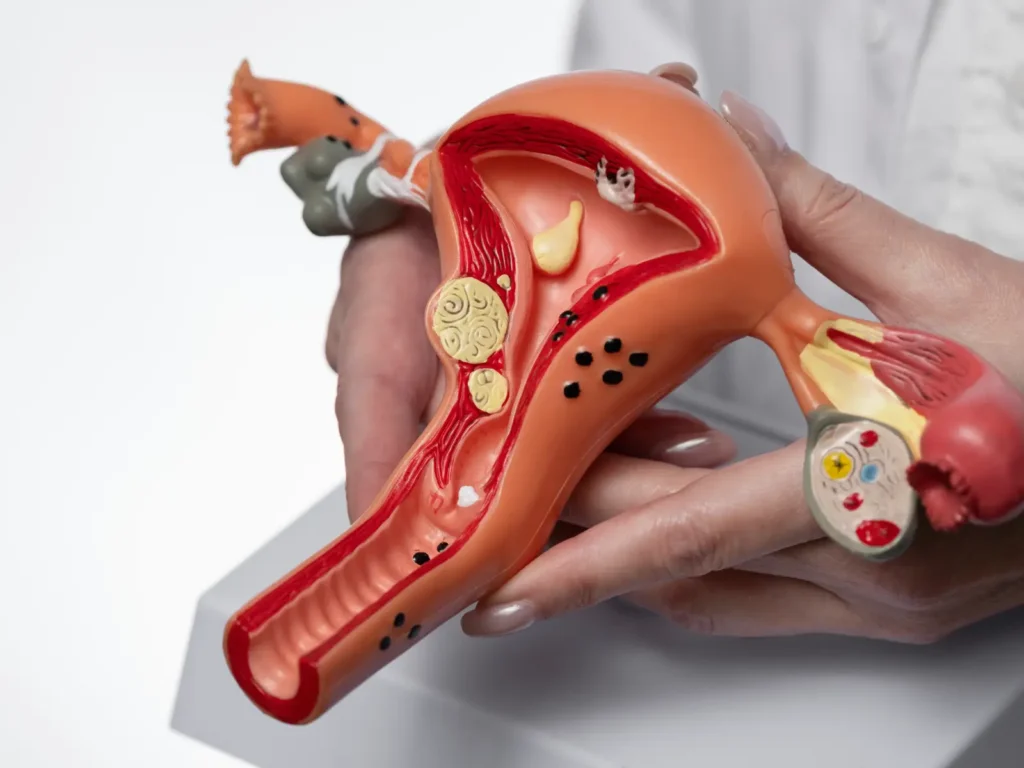
Reproductive health is a key part of human well-being and depends on the proper functioning of the endocrine system. At the center of this system is the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, which regulates processes such as gamete production, sex hormone balance, fertility, and sexual function. When hormonal signaling becomes disrupted, it can affect fertility, menstrual cycles, and overall reproductive function.
Other Application Areas

Peptide-based substances, known for their structural diversity and high biological activity, offer significant value beyond their well-established roles in metabolic regulation and immune modulation. They are increasingly applied in specialized fields such as respiratory health, cardiovascular protection, and experimental research. By enabling targeted mucosal repair, regulating cardiovascular signaling pathways, and serving as precise molecular tools for scientific studies, peptides overcome limitations of traditional therapeutics and enhance research innovation. Their advantages—high target specificity, low immunogenicity, and customizable synthesis—support their expanding impact across multiple scientific disciplines.
Neurological and Cognitive Health
The nervous system governs cognition, emotion, and overall body function through highly complex signaling and neurotransmitter networks. When these systems are disrupted—whether through degeneration, inflammation, or injury—conditions such as cognitive decline, anxiety, depression, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and neural trauma can arise.
Muscle and Tissue Repair
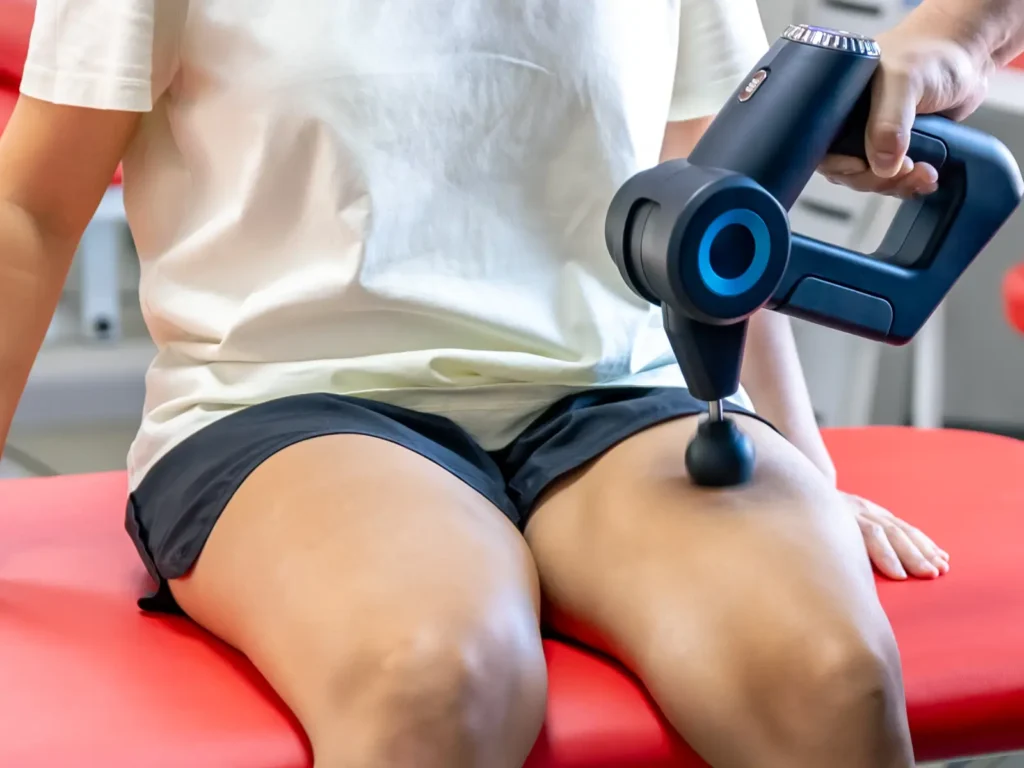

Muscle and tissue repair are essential biological processes responsible for maintaining mobility, structural strength, and recovery after injury. These processes rely on tightly coordinated mechanisms such as cell proliferation, extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, angiogenesis, and inflammation regulation. Key areas—such as muscle development, wound healing, joint repair, and recovery from sports injuries—depend on accurate modulation of satellite cells, fibroblasts, cartilage matrix metabolism, and neuromuscular junction repair.
Metabolic and Endocrine Regulation
The metabolic and endocrine systems work together to maintain energy balance, material metabolism, growth, and overall physiological stability. When this balance is disrupted, conditions such as diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and growth disorders can occur. Factors like poor diet, sedentary habits, lack of sleep, stress, and environmental triggers can disturb hormonal signaling, cause inflammation, and negatively affect metabolic health.
Immunity and Anti-inflammation
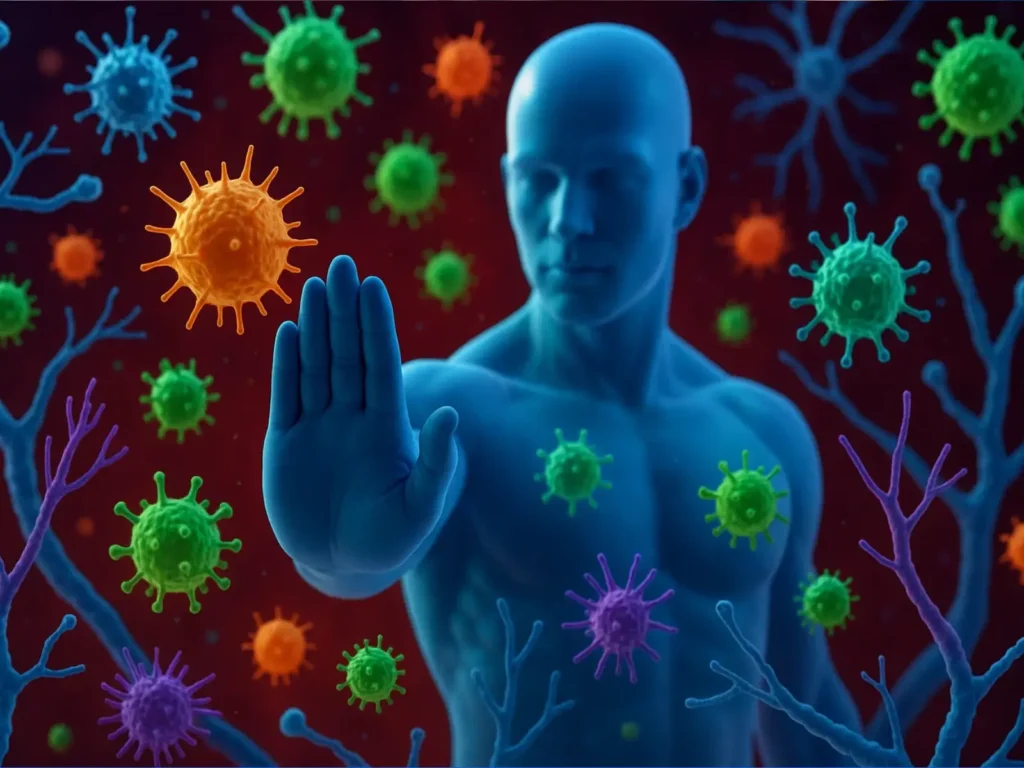

The immune system maintains balance in the body through a highly coordinated network of cells, receptors, and signaling molecules. When this system becomes dysregulated, it can lead to infections, chronic inflammation, or autoimmune disorders. Effective immune support and anti-inflammatory regulation require precise control over immune cell activity, inflammatory signaling pathways, and mechanisms that maintain immune tolerance.
Antioxidation and Liver Health
The liver is one of the body’s most important metabolic and detoxification organs. It performs essential functions including biosynthesis, energy storage, and the clearance of harmful substances. Factors such as oxidative stress, toxin buildup, and metabolic imbalance contribute to liver injury, fatty liver disease, and the development of fibrosis.
Peptides Purity
NUPEPS Peptides delivers peptides with purity levels exceeding 99%, achieved through advanced production technologies and a comprehensive.
Peptides and Amino Acids
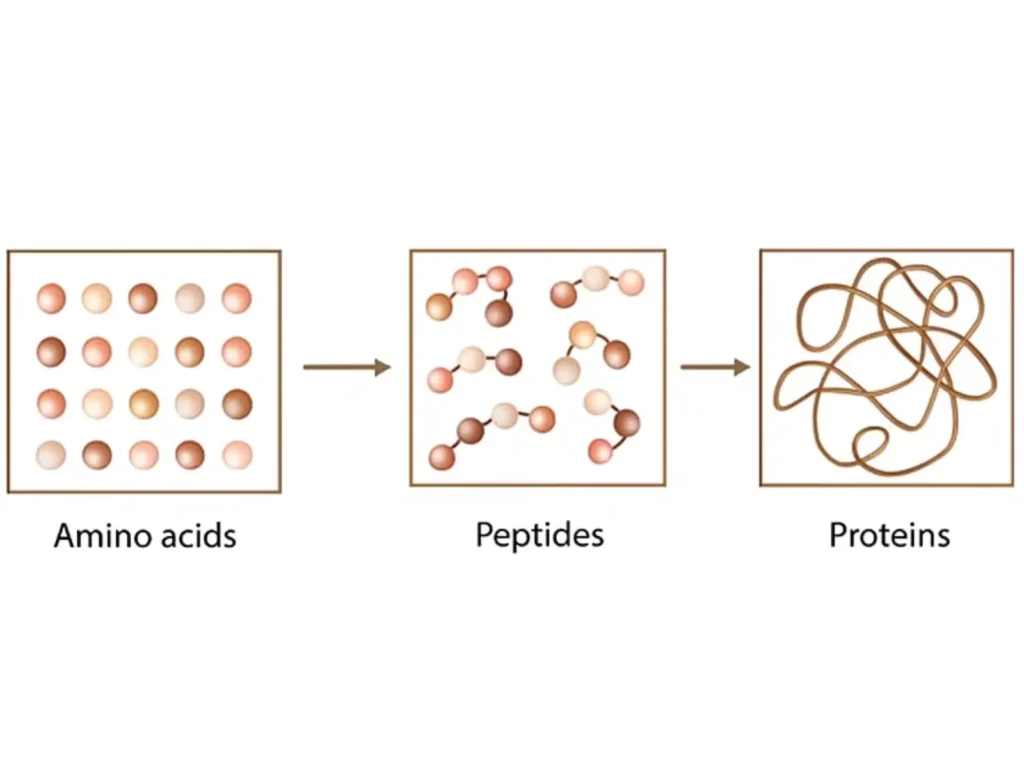
Introduction to Amino Acids and Peptides Amino acids are organic molecules that contain both an α-amino group (–NH₂) and an α-carboxyl group (–COOH). With the general structure RCH(NH₂)COOH, each amino acid’s properties are defined by the chemical nature of its side chain (R group). There are 20 naturally occurring amino acids involved in protein formation. […]
