Peptide Synthesis

Peptide synthesis is the process of assembling amino acids into defined sequences through the formation of amide (peptide) bonds. This enables the creation of custom oligopeptides and polypeptides with specific biological functions. As a core discipline of bioorganic chemistry, peptide synthesis encompasses:
Peptide Solubility
Peptide solubility describes the maximum amount of a peptide that can dissolve in a given solvent under defined temperature and pH conditions. It is typically expressed as mass concentration (g/L) or molar concentration (mol/L). Solubility is a fundamental physicochemical property that influences:
Peptide Bond
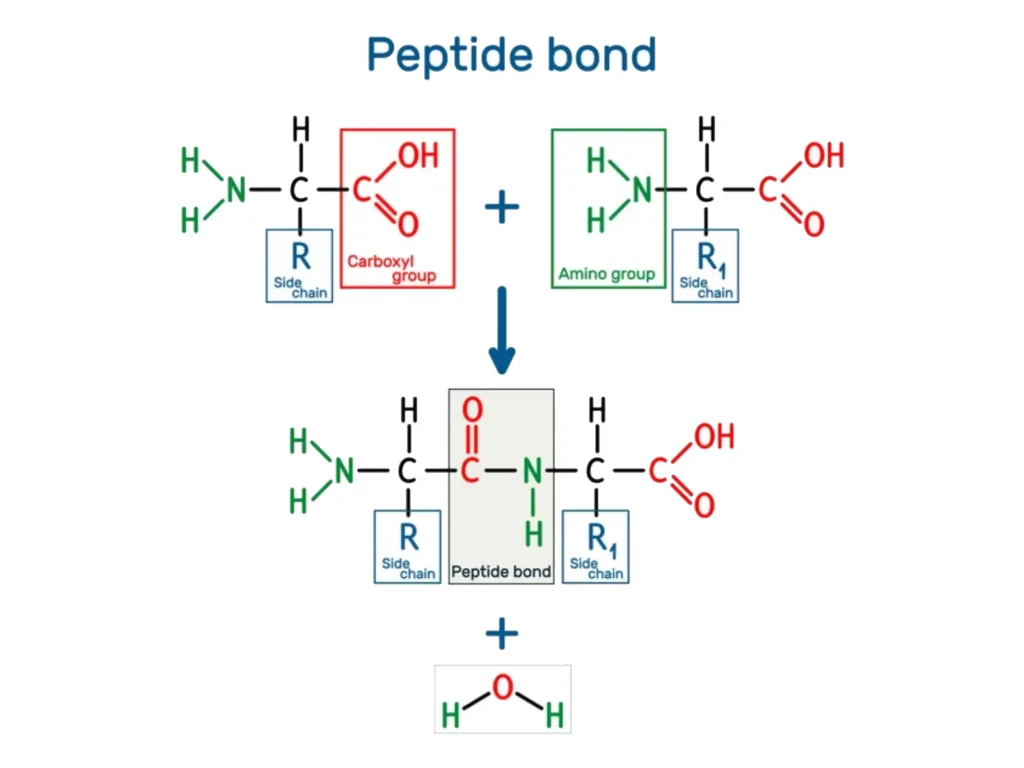
A peptide bond is a key covalent linkage found in proteins. It forms through a dehydration condensation reaction between the α-carboxyl group (α-COOH) of one amino acid and the α-amino group (-NH₂) of the next. Chemically, it is an amide bond.
This connection forms the backbone of a polypeptide chain: amino acids are linked from the N-terminus to the C-terminus through repeating peptide bonds. Because of partial double-bond character between the carbonyl carbon (C=O) and the nitrogen (-NH-), the peptide bond is rigid and planar. This rigidity is essential for how proteins fold into higher-order structures.
Introduction to Peptides
The word peptide originates from the Greek “πέσσειν” (péssein), meaning to digest. Peptides are compounds formed when amino acids link together through peptide bonds—a type of amide bond created during a dehydration condensation reaction between the α-carboxyl group of one amino acid and the α-amino group of another.
Peptides for research

Research peptides are synthetically designed molecules created in laboratories to support scientific investigation. Their primary role is to facilitate in vitro research, such as cell culture studies, molecular interaction analyses, and biochemical assays. While these peptides do not directly affect human or animal physiology, they are essential tools for understanding biological mechanisms, testing theoretical hypotheses, and screening potential molecular structures. By providing this foundational insight, research peptides help advance the early stages of drug discovery under strictly controlled laboratory conditions.
Peptide Storage

Peptide compounds are highly sensitive to environmental conditions due to their specific amino acid sequences and three-dimensional structures. Proper storage is essential to prevent chemical degradation, oxidation, and aggregation, thereby preserving structural integrity and biological activity. The peptide backbone is susceptible to hydrolysis, while side chains may react with moisture, oxygen, or microbial contaminants, which can lead to loss of function.
Peptide Purification

What Is Peptide Purification? Peptide purification is the process of isolating and refining crude peptide mixtures—whether produced through chemical synthesis or recombinant expression—to obtain high-purity target peptides. The goal is to eliminate impurities such as unreacted monomers, truncated or misassembled sequences, host-cell proteins, reaction by-products, and endotoxins. These contaminants can compromise peptide stability, alter biological […]
Anti-aging and Cosmetology

Aging and skin concerns develop through a combination of biological processes, including collagen loss, oxidative stress, melanin accumulation, telomere shortening, and reduced cellular energy production. Bioactive peptides offer targeted and highly compatible solutions by acting on these pathways with precision. Through structure-optimized or naturally-mimicking molecules, peptides help reinforce the skin barrier, support repair, improve texture, […]
Optimizing Cellular Energy Metabolism with Peptides

Learn how mitochondrial-targeted peptides enhance ATP production, improve energy metabolism, and support experimental studies on cellular function.
Peptides in Neuroprotection Research

Explore the potential of peptides in protecting neuronal cells, reducing oxidative stress, and advancing treatments for neurodegenerative diseases.
